原标题:美联储还等什么?
概括
[WhentheeconomycontinuestorecoverwhenwilltheFedtightenpolicy?】WebelievethattherearetwoconditionsfortriggeringtheFed’sreversaloperationtointerveneOneisthattheUSTreasuryyieldhit18%beforetheepidemicandtheotheristhattherisinglong-endinterestratehasledtocontinuedtighteningoffinancingconditionsandchaoticmarketconditions
Key points
March 17,MidlandReserve announced interest ratemeetingStatement to continue to maintain the federationfundinterest rateIn the 0-0.25% target range, at least 80 billion US dollars will be carried out every monthNational debtAnd 40 billion US dollars of MBS asset purchase scale, in line withmarketexpected.
This interest meetingMidlandChu faces a problem,How to objectively judge the progress and prospects of the current economic recovery while avoiding unnecessary hawkish associations in the market?
We understand this interest meetingMidlandChu WeiArtistically released three signals,Real economyStill in the early stage of restoration,currencyRegulate the overall maintenance of dovish, long-endinterest rateIt’s still in the acceptable range.
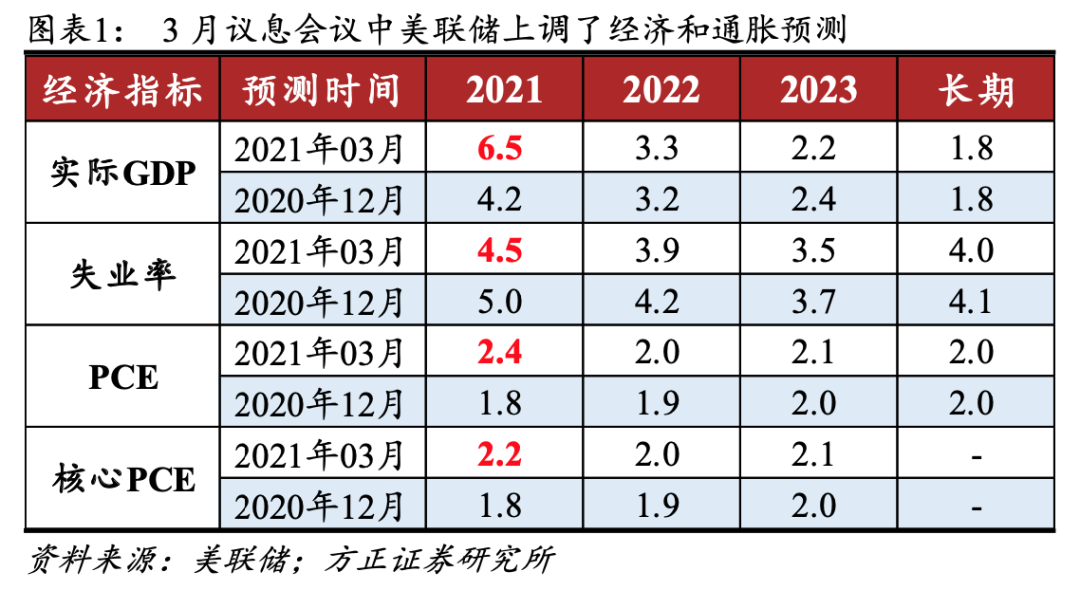
The Fed raised its economic and inflation expectations while sending dovish signals.
The Fed forecasts actual 2021GDPThe growth rate rose to 6.5%,unemploymentRate dropped to 4.5%, core PCEYear-on-yearRose to 2.2%.
But for the moment, the Fed believes that the foundation of economic recovery is not yet solid, and there is no need to tighten monetary policy immediately. The Fed is also worried that the market will misunderstand the marginal changes in monetary policy, which will further affect economic and financial stability.
Powell believes that the rise in inflation this year is mainly due toBase effectAnd short-termsupplyThe impact of restrictions and demand rebounds will fall in the future.
The Fed maintains its dovish stance on the long endinterest rateStay tolerant on the upside.
The market is very concerned about whether the Fed will intervene in the upward trend of long-end interest rates. In response to this issue, the Fed responded that the SLR exemption policy is likely to be postponed. Considering that the current overall financing conditions are still relatively loose, the Fed believes that no additional operations are necessary.
We believe that there are two conditions for triggering the Fed’s reversal of operations to intervene. One is that U.S. Treasury yields hit 1.8% before the epidemic, and the second is that rising long-end interest rates have led to continued tightening of financing conditions and market conditions.
The future operation of Fed regulation under the background of continuous economic recovery.
Based on the experience of the previous round, the Fed’s tightening of monetary policy will follow the operating sequence of “release the Taper signal-execute Taper-raise interest rates-shrink the balance sheet”.
If the economy recovers steadily during the year, the Fed may release the Taper signal at the December interest rate meeting, which will trigger a new round of rapid rise in U.S. bond yields.
However, if the Fed implements a reversal operation to intervene in long-end interest rates during the year, it means that the pace of US economic recovery will slow down, and the Taper signal will be postponed to 2022. The US bond yield may fluctuate around 1.8% throughout the year.
text
1. The art of the Federal Reserve, sending dovish signals while raising economic and inflation forecasts
The Fed faced a difficult problem in this interest rate meeting, that is, how to objectively judge the progress and prospects of the current economic recovery while avoiding unnecessary hawkish associations in the market.
Since the interest rate meeting in December last year, the United States has launched two rounds of large-scale fiscal stimulus totaling US$2.8 trillion. The epidemic has improved significantly, vaccination has accelerated, crude oil and bulkProductpriceIf it continues to rise, the Fed will naturally raise its economic and inflation forecasts.2021Real GDPThe growth rate rose to 6.5%,unemployment rateDown to 4.5%, core PCE rose to 2.2% year-on-year.
In addition, 4-5 FOMC members have raised the number of interest rate hikes in 2022 and 2023. The market will inevitably carry out a hawkish interpretation, and it is precisely this that has been expected. Before the announcement of the meeting statement, the yield on the 10-year U.S. Treasury once surpassed 7BP.
Against the backdrop that the foundation of the current economic recovery is not yet solid, the Fed has no intention of tightening policy, and it is also worried that market misunderstandings will affect economic and financial stability. The meeting statement emphasized that the sectors most affected by the epidemic are still weak, and inflation is still running below 2%.
In the speech and Q&A at the press conference, Powell believed that the upward inflation this year is mainly due to the base effect and short-term supply constraints and demand recovery. The core PCE will fall to 2.0% in 2022 year-on-year.Powell does not have much confidence in achieving the 2% long-term inflation target. He believes that inflation expectations and actual inflation are two different things, and will discuss them after actual inflation rises to 2%.
The interest rate hike forecast in the dot plot is highly uncertain, and the actual rate of interest rate hike still depends on the real economic performance.For tapering (Taper) QE, the Fed will communicate in advance, and the market does not need to worry prematurely.

2. Maintain a dovish stance, but still tolerate the rise of long-end interest rates
The market is most concerned about whether the Fed will intervene in the recent fast-rising long-end interest rate. Although the intervention implied in this interest rate meeting is not as eagerly expected by the market, the Fed’s attention and contingent operations on the upward trend of long-term interest rates mean that the fastest period of upward long-term interest rates has basically passed.
The SLR exemption policy will expire at the end of March,If the maturity is not renewed, it will trigger a sell-off of U.S. Treasuries and further push up long-end interest rates.Powell said that the results will be announced in the next few days, and the market is expected to be optimistic.Apart from this, the Fed has no other actions.
Compared with the central banks of major economies such as Europe and Japan, the Fed has shown a higher tolerance for fast-rising long-end interest rates. The main reason is that the current overall financing conditions are still relatively loose. The Fed believes that the current monetary policy is satisfactory and there is no need for additional operations.

3. If the dovish stance changes, the Fed’s two judgment conditions for intervening in long-term interest rates
First, the 10-year U.S. Treasury yield rose to the pre-epidemic (January 2020) level of 1.8%.At that time the Fed might start to considerInterest rate levelIs it too high for the economy that is still recovering?
Secondly, the rising long-end interest rate has led to continued tightening of financing conditions and chaotic market conditions.Harm to the FedEmploymentAnd the achievement of the dual goals of inflation.Current mortgage andenterpriseAlthough bond interest rates have risen, they are still at a low level. The fall in the price of mid- and long-term Treasury bonds and the adjustment of high-value growth stocks are only part of the market.

4. When the economy continues to recover, when will the Fed tighten its policy?
Large-scale fiscal stimulus and vaccination may achieve herd immunity in the middle of the year. The market is worried that the US economy will overheat. Five-year and 10-year inflation expectations hit new highs since 2008 and 2014, respectively. It is expected that the Federal Reserve may tighten the currency during the year. policy.
In the previous round of normalization of monetary policy, the Fed’s policy tightening had a clear sequence, first communicating with the market about Taper, then actually implementing Taper, then raising interest rates, and finally shrinking the balance sheet.After learning the lessons of Bernanke’s miscommunication in May 2013 that triggered the tapering panic (Taper Tantrum), the Fed’s relevant operations will be more cautious.
If the economy during the year is as expected by the Fed,The unemployment rate has dropped to 4.5%, and core inflation has risen to 2.2%. The Fed may release a Taper signal during its December meeting on interest rates. At that time, it will trigger a new round of rapid rise in U.S. Treasury yields.
If the market expects during the year,The Fed’s implementation of reversing operations to intervene in long-end interest rates means that the pace of US economic recovery has slowed, and the Taper signal will be postponed to 2022. Reversing the operation is policy easing, and Taper is policy tightening. It is impossible for the Fed to experience such a large policy shift within a year, otherwise it will cause huge market expectations and economic and financial fluctuations. In this case, the U.S. Treasury yield may fluctuate around 1.8% throughout the year.

risk warning
The US economic recovery exceeded expectations; the US fiscal stimulus exceeded expectations; the Fed’s monetary policy exceeded expectations.
(Source: Macro Zhidao)
(Editor in charge: DF537)
Solemnly declare: The purpose of this information released by Oriental Fortune.com is to spread more information and has nothing to do with this stand.