概括
[Non-agriculturalultimateprospect:themanufacturingindustryalonecanhardlysupportgoldbullsorfaceagoodopportunitytocounterattack?】At21:30BeijingtimeonFriday(March5)theUSDepartmentofLaborwillannouncetheFebruarynon-agriculturalemploymentreportintheUnitedStatesThecurrentmarketexpectsthatthenumberofnon-agriculturalemploymentwillincreaseby198000andtheunemploymentratewillremainunchangedat63%Hourlywagesincreasedby53%year-on-year(Huitongcom)
At 21:30 Beijing time on Friday (March 5), the US Department of Labor will announce the US non-agricultural employment report for February. The current market expects that the number of non-agricultural employment will increase by 198,000, and the unemployment rate will remain unchanged at 6.3%. Hourly salaryYear-on-yearAn increase of 5.3%.
However, judging from past non-agricultural performance, economic data and fundamentals of the United States in the past month, the possibility of this non-agricultural performance being worse than expected is slightly higher. The price of gold has continued to fall recently and hit a new low in the past nine months. At this time, investors need to beware of the gold bulls counterattack.
Last non-agricultural performance
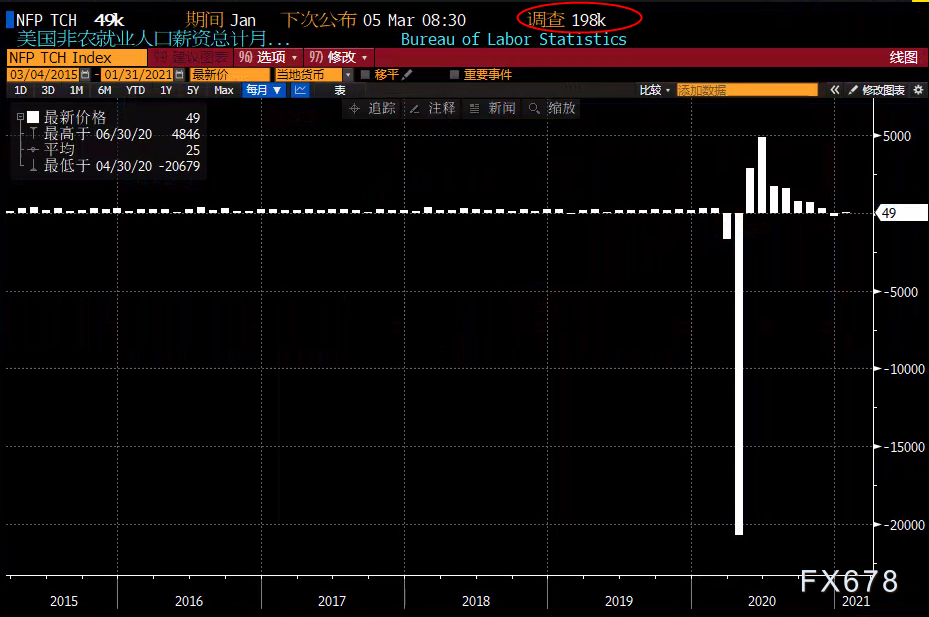
After decreasing by 227,000 in December, non-agricultural employment only increased by 49,000 in January, and the unemployment rate dropped to 6.3%, which partly reflects that more people leavelaborPower market.
The U.S. employment growth rebounded moderately in January, and the decline in non-agricultural jobs in December was even more severe than initially expected. The U.S. Department of Labor’s employment report released on February 5 showed that,manufacturingAnd the construction industry has fewer jobs, these two industries have been supporting the economy. The number of unemployed in restaurants and bars is also increasing. Retailers and employers in the transportation industry are also laying off workers. Millions of Americans are experiencing long periods of unemployment and permanent unemployment, while others have given up looking for work.
Specific data show that non-agricultural jobs in the United States increased by 49,000 in January. The December data was revised to a decrease of 227,000, rather than the previously reported decrease of 140,000. The number of employed people is 9.9 million below the peak in February 2020. In the 12 months to March 2020, the U.S. economy created 250,000 fewer jobs than previously estimated.

(List of historical performance of non-agricultural employment data)
Although the unemployment rate fell from 6.7% in December last year to 6.3% in January this year, this is because people mistakenly classify themselves as “have a job but did not go to work,” and this data continues to be underestimated. Without this error, the unemployment rate would be approximately 6.9%.
More than 4 million Americans were unemployed for more than six weeks, accounting for 39.5% of the unemployed in January. The number of permanent unemployed persons increased from 3.4 million in December last year to 3.5 million. The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) estimates that employment will not return to pre-epidemic levels before 2024.
The non-agricultural materials are difficult to be beautiful this time, and employment in the service industry is difficult to improve in the short term, or it may pour cold water on the dollar bulls
The February non-agricultural employment report will be the first complete monthly employment report of the new US President Biden after taking office, and it has received exceptional expectations from all walks of life in the market.However, the industryAnalystHowever, he gave a pessimistic forecast in advance. It is believed that after the employment data in December and January continues to be sluggish, it is still difficult to record a significant improvement in February. On the one hand, the impact of the epidemic still exists, and on the other hand, it suffered severe cold during the data investigation. Blizzard weather may also cause additional shocks to employment data.
The current market consensus is that non-agricultural jobs in the United States will increase by 198,000 in February, and the unemployment rate will remain unchanged at 6.3%. The specific employment status depends on the progress of the states to relax epidemic control measures. Since the end of last year, when the epidemic broke out again, service industries such as catering and accommodation have once again become unemployment-hit areas.And includeMidlandOfficials such as President Powell and the new US Treasury Secretary Yellen have repeatedly emphasized that sluggish employment is still the biggest weakness facing the US economy.MidlandReserve officials have previously emphasized that the pace of US employment recovery has been released again in recent months. Therefore,currencyUnder this background, there is no possibility that the easing policy support will be removed.

Despite this, US bond yields are still rising recently under strong bets on economic recovery. The premise that investors are highly optimistic about the economy is based on one point. They expect that with the help of vaccines, the order of economic activities in the United States will return to normal as soon as possible. In this way, everyone will return to the pace of life in the past and patronize gyms, bars and yoga Facilities such as museums, and this will eventually restore the vitality of the service industry that was previously half-paralyzed.
The service industry in the United States employs more than 70% of the employed population in the entire society. Only when the operation of this industry returns to the right track can the overall economy and job market get out of the quagmire. Based on optimistic expectations for the prospects of vaccine applications,MidlandThe Reserve Bank expects that the unemployment rate will fall back to below 5% by the end of 2021.Goldman SachsBusiness organizations such as Deutsche Bank are more optimistic in their forecasts, believing that the unemployment rate is expected to fall back to the 4% range by then.
Long-term forecasts cannot change the current predicament. The data to be released this Friday may still pour cold water on the already overheated market sentiment. The data is expected to continue to highlight the plight of employment in the US service industry. At present, the total employment population in the service industry in the United States is as much as 122 million, but this is still a full 9 million less than the beginning of the epidemic last year. Therefore, non-agricultural employment is expected to increase by only 198,000, which means that the current distance is completely digested. The huge number of unemployed people still has a long way to go, which will inevitably make observers suspicious of the previously overly optimistic economic and employment goals.
24 investment banks look ahead to US non-agricultural February: the job market may show signs of stagnation

The forecasts of 24 large investment banks show that the major investment banks’ expectations for the growth of non-agricultural employment population in February are not negative, but the expected gap between investment banks is large. Specifically, the US non-agricultural employment growth rate after the seasonal adjustment in February It is expected to be between 60,000 and 410,000, the unemployment rate is expected to be between 6.2% and 6.5%, and the average hourly salary increase is expected to be between 5.1% and 5.4%.
Five big data guide the direction
1. The U.S. manufacturing sector recorded the fastest growth in three years in February
The U.S. manufacturing industry recorded the fastest growth in three years in February. According to data released by the American Institute of Supply Management on Monday, FebruaryManufacturing IndexIt rose to 60.8 from 58.7 in January, which was higher than the median estimate of 58.9 by economists. An index above 50 indicates expansion.
ISM manufacturingenterpriseThe chairman of the investigation committee, Timothy Fiore, stated in a statement that the company and itssupplierfacinglabor forceMarket difficulties continue to limit the growth of the manufacturing industry,supply chainBefore the employment level and factory operations return to normal, this will still be the main factor that is not conducive to production growth.
It is worth mentioning that the ISM’s new order sub-index rose to 64.8 in February from 61.1 in January.Factory acquiredExitOrders increased, and outstanding orders surged. Affected by this, the company hired more staff last month.
The manufacturing employment sub-index rose to 54.4 from 52.6 in January, the highest since March 2019.
2. The U.S. service industry’s growth rate in February was the slowest in nine months
The growth rate of the US service industry fell to its lowest level in nine months in February, as the severe cold weather that swept across most of the country restricted activities.
Data released on Wednesday showed that the Institute of Supply Management Service Industry Index fell to 55.3 from a nearly two-year high of 58.7 in January. Data above 50 indicates growth. The February data was lower than expected by all economists surveyed.
New orders and business activity indicators also fell to their lowest levels since May. Although many service providers are still constrained by the epidemic, the downturn in February was due to weather factors. The polar vortex disrupted the supply chain, caused power outages, and affected commerce in some areas.
The polar vortex brought record low temperatures to more than 9,000 cities in the United States. The most serious situation occurred in Texas, where the power grid was overwhelmed and thousands of homes lost their lighting, heating and water supply.
The slowdown in service sector activity may be temporary, as the ISM reserve orders index rose to a six-month high of 65.2, whileExport demandThe indicator reached its strongest level since June.
Service industry indicators also show material paymentspriceIt jumped to 71.8 in February, the highest level since September 2008. Delivery time has also been extended. Manufacturing data released by ISM on Monday showed that the input cost of the factory is also the highest since 2008.
Both reports indicate that supply shortages and labor constraints are still obstacles in many industries.
The ISM service sector employment index showed that the growth rate slowed in February, falling from 55.2 to 52.7.
3. ADP data shows that the number of new jobs created by U.S. companies in February was lower than expected
The number of new employees in US companies in February was lower than expected, highlighting that although the growth of new crown infection cases has slowed in recent weeks, the recovery of the labor market is still difficult.
According to data released by the ADP Research Institute on Wednesday, the number of corporate employment increased by 117,000 that month. The median forecast by survey economists is an increase of 205,000 people. The increase in January was revised upward to 195,000.
These figures show that the constraints imposed by the pandemic on businesses and economic activities are dragging down employment growth. Even so, many economists expect that the labor market will continue to improve in the coming months as vaccination speeds up and concerns about the virus ease.
ADP chief economist Nela Richardson said in a statement, “The labor market continues to recover comprehensively but weakly. We see large-scalethe companyThe impact of the epidemic is being felt more and more, while employment growth in the commodity production sector has stagnated. “
According to ADP data, employment growth in February was driven by the service industry. The number of employees in the service industry increased by 131,000 that month. At the same time, the number of employment in commodity-producing companies fell by 14,000, with the manufacturing industry leading the decline.
4. The number of people applying for unemployment benefits for the first time in the U.S. rose slightly last week
In the week ending February 27, the number of people applying for unemployment benefits for the first time increased by 9,000.
The number of people applying for state unemployment benefits for the first time in the United States rose slightly last week, highlighting that the epidemic has continued to pressure the recovery of the employment market.
Data released by the US Department of Labor on Thursday showed that in the week ending February 27, the number of first-time jobless claims increased by 9,000 to 745,000. Economists estimate that it is 750,000 people. The number of unadjusted first-time applicants increased by more than 31,500.
As of the week of February 20, the number of people who continued to apply for unemployment benefits decreased from 4.4 million in the previous week to about 4.3 million.
The latest data show that the labor market is still in the quagmire of the epidemic crisis, and many industries have reduced economic activity. However, the current rate of new crown infection in the United States is declining, and more and more Americans are vaccinated against the new crown. As the economy recovers, the number of unemployed persons is expected to decrease in the next few months.
Weather factors may also affect the number of unemployed. Last week, the number of people applying for unemployment benefits in Texas for the first time increased by nearly 17,800 compared with the previous week, the highest increase among all states. The severe cold weather in the previous week may cause the unemployed to postpone or fail to submit an application for unemployment benefits. This impact is also reflected in the latest report.But it may not be fully reflected in this non-agricultural employment report
5. The number of layoffs dropped to a low in more than a year
In another report released on Thursday, the globalReemploymentThe company Challenger, Gray & Christmas stated that the US company announced in February that it would lay off 34,531 employees. This is the lowest level since December 2019 and is lower than the 79,552 people in January.
Wells Fargo Securities senior analyst Sarah House said, “After a difficult winter, the employment situation has begun to stabilize again.”
Judging from the above five data, it is expected that the number of non-agricultural employment growth in the United States in February will be limited. In the context of the sharp decline in US stocks and the preparation of the US President’s 1.9 trillion stimulus plan, spot gold may be supported by bargain hunting. However, from a technical point of view, the gold price still has further downside action in the short-term. It is currently testing the key support of 1689.32 (61.8% retracement of the 1451-2075 rally). Investors should pay attention to whether the close can hold this key position. Further support is near the low of 1670.98 on June 5.
Summary of Institutional Views
Goldman Sachs: The number of non-agricultural employment will increase by 225,000 in February, while the unemployment rate will remain unchanged at 6.3%;
①Famous investment bankGoldman SachsIt is expected that the number of non-agricultural employment in the United States will increase by 225,000 in February, and the unemployment rate will remain unchanged at 6.3%;
②Goldman Sachs pointed out that the decline in infection rates andbusinessThe relaxation of restrictions may support employment growth in epidemic-sensitive industries;
③Due to the negative calendar effect, Goldman Sachs estimates that the monthly average hourly wage rate in February in the United States is 0.1%, which is lower than the previous value of 0.2%.
Financial website Forex.Com: Non-agricultural materials increased by 185,000 in February. If it is stronger than the expected market, it may sell the euro against the US dollar;
① According to the financial website Forex.Com, despite recent bleak employment data in the United States, economists are optimistic that with the increase in vaccinations and the approval of another stimulus bill by Congress, the U.S. economy will begin to accelerate sharply in the next few months. ;
② Economists predict that non-agricultural employment will reach 185,000 in February, and the average monthly rate of hourly wages in the United States in February is 0.2%;
③The website also pointed out that if the non-agricultural employment data is stronger than expected,TradersMay treat the euro against the dollar as a possible sell-off
Research company: predicts that the US non-agricultural sector may rebound in February, or an increase of 180,000;
①Raffi Boyadjian, an economist at XM Investment Research, predicts that after a few months of depression, the US labor market is expected to regain some momentum in February, and the February non-agricultural report may show strong employment growth in the United States;
②However, in the near futureBondAfter the market crash, a series of optimistic economic data may once again push up U.S. Treasury bond yields and push up the U.S. dollar;
③The latest analysts predict that the US economy added 180,000 jobs in February, up from 49,000 in January. The unemployment rate in February is expected to remain unchanged at 6.3%, because more people may rejoin. Labor force
Fxstreet analyst Joseph Trevisani: predicts that the US non-agricultural increase in February will increase by 180,000, and the unemployment rate will remain at 6.3%;
①Fxstreet analyst Joseph Trevisani predicts that the US non-agricultural increase in February is expected to increase by 180,000, which is much better than the average decrease of 89,000 in December and January, but far lower than the increase of 473,000 in October and November 2020;
②In addition, he predicts that the unemployment rate in the United States will remain unchanged at 6.3% in February
Fxstreet analyst Kenny Fisher: After the January downturn, it is predicted that the US non-agricultural increase will increase by 133,000 in February;
Financial website Fxstreet analyst Kenny Fisher wrote that the US non-agricultural increase in January was only 49,000, and the non-agricultural increase in February was predicted to increase by 133,000. It is predicted that the monthly average hourly wage rate in the United States in February is 0.2%, which is consistent with the previous value.
Fxstreet analyst Yohay Elam: Non-agricultural increase of 182,000 in February, reaching or exceeding this number will push up the dollar;
①Fxstreet analyst Yohay Elam said that it is expected that the United States will add 182,000 jobs in February, and that U.S. employment is a slow recovery process;
②He also pointed out three reasons for the low estimate: the employment situation in the United States is relatively weak; the leading indicators are weak, and the latest ADP data is lower than expected, only 117,000 jobs have been added; economists have commented on the past three months. The non-agricultural employment data is too optimistic and will now be very cautious;
③Yohay Elam believes that if the non-agricultural real increase in February is about 182,000, the U.S. dollar still has room to rise; if the actual data exceeds 182,000, it will become a bigger booster for the U.S. dollar; however, if the non-agricultural decline in February is lower than 182,000, if it is less than 100,000, the U.S. dollar will go down
Wall StreetDaily investigation: US non-agricultural may increase by 210,000 in February;
According to the beautyGuohuaAccording to a survey conducted by the Street Journal on March 1, the current market forecasts that the US non-agricultural increase in February will increase by 210,000 (previously 49,000), the unemployment rate in February will be 6.3% (previously 6.3%), and the monthly average hourly wage rate in February will be 0.2 % (Previous value 0.2%), average hourly wage annual rate 5.3% (previous value 5.2%)
SMBC: US non-agricultural employment data may determine the next trend of US Treasury bonds;
① Chief of SMBC Nikko Securitiesinterest rateStrategist Chotaro Morita wrote in a report that it is too early to say that the US Treasury turmoil has peaked. The US non-agricultural employment data scheduled to be released on Friday may help determine the direction of the market.
② According to the report, the drop in U.S. Treasury yields last Friday may be due to adjustments by participantsPosition。
③ The report pointed out that, unlike the price reduction turmoil in 2013, the Fed officials lacked “rescue speech” this time and declared that the market chaos is over. Be cautious
④ The report also pointed out that the fluctuations in US yields last week may have been excessive. Participants are waiting for the number of non-agricultural employment in the US to assess future trends.
⑤ The report also stated that in the past, when yields fluctuated, employment data had a significant impact on U.S. debt. The U.S. 10-year Treasury bond yield may stabilize in the region of 1% and may be around 1.2%-1.25%.
⑥ Chotaro Morita believes that after taking actions last week, participants may increase the target range for the 10-year US Treasury bonds, which will increase the bargain-hunting target level
(Source: Huitong.com)
(Editor in charge: DF318)
Solemnly declare: The purpose of this information is to spread more information, and it has nothing to do with this stand.